Diagnostic methods

DIAGNOSTIC ULTRASOUND
Using diagnostic ultrasound, one can visualize the soft tissue structures including muscle, tendon, ligament, fascia, in exquisite detail, achieving clear and precise diagnostic information.
It enables identification of inflammation, tears, ruptures, fluid collections, soft tissue masses and other lesions. High frequency ultrasound as available here, using the Mindray 7 system, allows one to visualize not only tendon tears, but the internal fibrous structure, enabling earlier diagnosis of potential problems.
The investigation is particularly useful in the specialties of sports medicine, rheumatology and orthopedics.
Ultrasound can be used to guide injections accurately to target soft tissues more specifically. This has been shown to increase recovery rate.
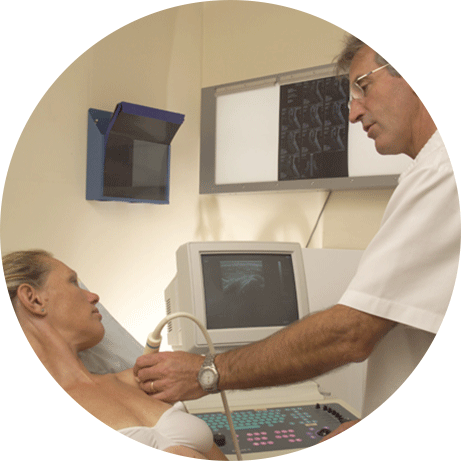
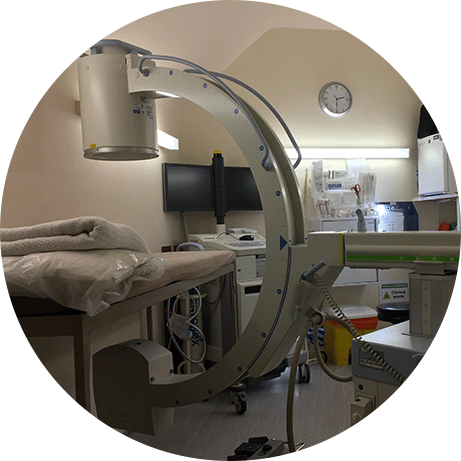
FLUOROSCOPY
In the fluoroscopy suite the doctor is able to do any injections under X ray guidance. A nurse will supervise the patient who is may be under light sedation.
It is also useful to assess joints and the bony skeleton for acute fractures or other reactions, including spinal or joint instability.
This means that procedures which normally would have to take place in hospital can be achieved in a more relaxed setting.
Our fully equipped X-ray suite uses a C arm image intensifier to enable the operator to perform targeted injections such as nerve root blocks, facet joint injections, prolotherapy, selective epidurals and radio frequency lesioning (for chronic mechanical back and neck pain). Such facilities are important for safety and accuracy particularly in the spinal area.
DISCOGRAPHY
In some patients imaging such as MRI and CAT scan do not reveal the expected disc prolapse or herniation but simply show small disc bulges, degenerative changes and internal tears of the disc fibre. Some of the discs can be a source of continuing back pain and referred pain to the limb.
If the problem is severe and chronic and has not responded to standard physical therapies and other measures then the disc can be tested to diagnose whether it is the source of the exact pain the patient is complaining of.
This procedure is done as a day case under X-ray control when a spinal needle is guided into the centre of the disc under local anaesthesia. X-ray views are taken both from the back and the side to reveal the flow of radio-contrast material as it is injected into the disc.
Pressure measurements are made during the injection and the patient is asked repeatedly whether the increased pressure in the disc is causing pain (normal discs do not hurt) and if so whether the pain is similar or the same as the pain that he or she is complaining of. If this is the case a small dose of local anaesthetic and corticosteroid usually combined with antibiotic is injected into the disc to assess how long pain relief can be achieved. Some patients’ problem settle on this measure alone, so for a minority of patients it can be therapeutic.
With other patients the pain returns either within a few hours or a few weeks of the injection which indicates the need for a more permanent procedure to reduce disc pain. At the present time this usually requires referral to a spinal surgeon for an anterior fusion procedure or disc replacement, but there are now minimally invasive treatments such as nucleoplasty, cold RF/Gelstixs implants which can be done at our facility and are relatively safe although remain to be proven. Please discuss these options with Dr. Tanner at the clinic.
If you have further questions please contact us.
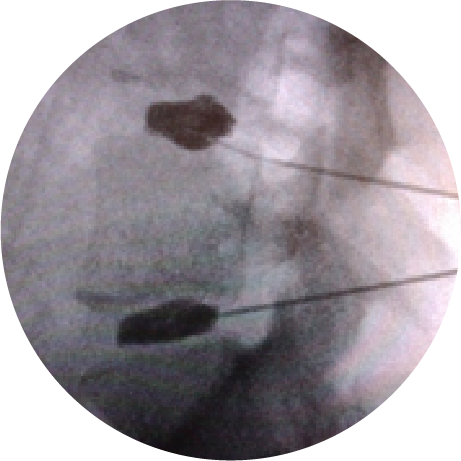
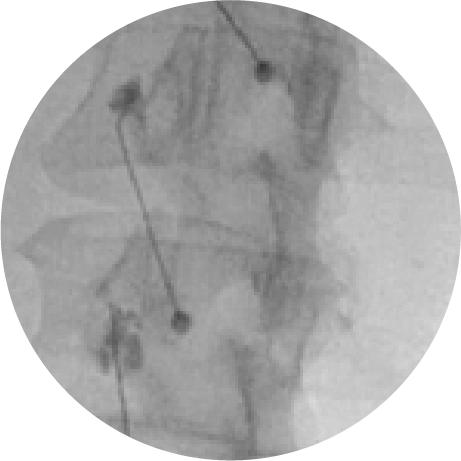
MEDIAL BRANCH BLOCKS
In order to make a definite diagnosis of spinal facet joint pain the small nerve branches to the suspect joints are anaesthetised with short and long acting local anaesthetics on two separate occasions under fluoroscopic guidance. More than 80% relief on each occasion is required to justify proceeding to Radiofrequency denervation.
It is a relatively quick and not very painful procedure which is completed as an outpatient.
IMAGING INVESTIGATIONS
This includes MRI scan (above) in open or closed scanner – most useful to asses soft tissues, nerves, disc herniation, bone marrow health.
Low price scans available for non insured patients for as little as £200 in London, Bournemouth £280, Cheltenham (£200). Open scanners available at Croydon, London and Bournemouth.
CT scan – for detailed viewing of bone anatomy in 3D
SPECT scan – for diagnosing detailed location of ‘hotspots’ in spine indicating possible pain source
Bone Isotope scan – to survey whole skeleton for bone pathology
Bone densitometry – to diagnose osteopaenia and osteoporosis.


LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS
Blood, urine and synovial samples taken here at the clinic and sent to Doctors laboratory London/ Manchester for every conceivable test at economical prices.
Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies – available here with Dr Chris Moore
What are electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies?
Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies are tests that measure the electrical activity of muscles and nerves. Nerves send out electrical signals to make your muscles react in certain ways. As your muscles react, they give off these signals, which can then be measured.
• An EMG test looks at the electrical signals your muscles make when they are at rest and when they are being used.
• A nerve conduction study measures how fast and how well the body’s electrical signals travel down your nerves.
EMG tests and nerve conduction studies can both help find out if you have a disorder of your muscles, nerves, or both. These tests can be done separately, but they are usually done at the same time.
Other names: electrodiagnostic study, EMG test, electromyogram, NCS, nerve conduction velocity, NCV
The spine
Disclaimer
This flow chart is intended as a guide only. We cannot accept any responsibility for decisions, actions or outcomes arising therefrom.